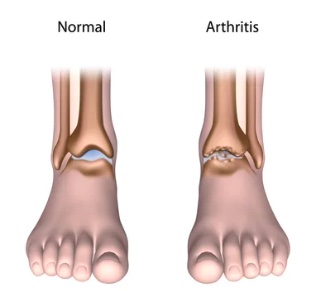
Foot or ankle arthritis is a condition characterised by inflammation and damage to the joints in the foot and ankle. Arthritis can affect any joint in the foot or ankle, including the ankle joint, the subtalar joint (between the heel and ankle), and the small joints of the toes. The most common types of arthritis that affect the foot and ankle are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear on the joints over time, leading to the breakdown of cartilage and bone.
Causes of foot or ankle arthritis
The causes of foot or ankle arthritis can vary depending on the type of arthritis. The most common types of arthritis that affect the foot and ankle are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear on the joints over time, leading to the breakdown of cartilage and bone. Risk factors for osteoarthritis in the foot and ankle may include:
Age: As people age, the risk of developing osteoarthritis increases.
Genetics: Osteoarthritis can run in families, suggesting a genetic component to the condition.
Injury: Previous injuries to the foot or ankle can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
Overuse: Repetitive motions or overuse of the foot and ankle can lead to joint damage and osteoarthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation and damage. The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not fully understood, but risk factors may include:
Genetics: Rheumatoid arthritis can run in families, suggesting a genetic component to the condition.
Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop rheumatoid arthritis.
Age: Rheumatoid arthritis can develop at any age, but it most commonly affects people between the ages of 40 and 60.
Smoking: Smoking may increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
Other types of arthritis that can affect the foot and ankle, such as gout or psoriatic arthritis, may have different underlying causes.
Overall, the causes of foot or ankle arthritis can be complex and multifactorial, involving a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent further joint damage.
Symptoms of foot or ankle arthritis
Symptoms of osteoarthritis in the foot and ankle can include pain, stiffness, swelling, and difficulty walking or standing for long periods of time.
Diagnosing foot or ankle arthritis
Diagnosis of foot or ankle arthritis may involve a physical examination, X-rays, or other imaging tests to evaluate the joint damage and assess the severity of the condition.
Treatment for foot or ankle arthritis
Treatment options for foot or ankle arthritis may include medication to relieve pain and inflammation, physiotherapy to improve joint mobility and strength, and the use of assistive devices, such as orthotics or braces, to support the affected joints. In more severe cases, surgery may be recommended to repair or replace damaged joints.
These factors including treatment options will all be discussed with you in consultation with Dr Singh.
 Christmas Operating Hours
Christmas Operating Hours 















