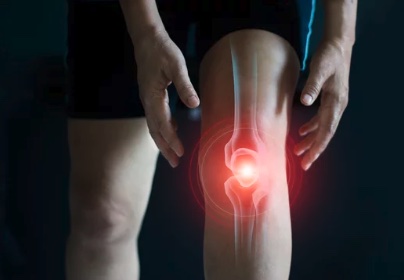
The knee has four major ligaments that make up the knee joint complex including the medial collateral ligament (MCL) which sits outside of the knee joint, on the inside of the knee. This ligament extends from the end of your femur (thigh bone) to the top of the tibia (shin bone). The MCL’s job is to allow your knee to rotate, while keeping it stable and from collapsing inwards.
Causes of an MCL tear or injury
An injury to the MCL occurs when an extreme force is placed on the outer side of the knee, causing the ligament on the inside to stretch or tear. Athletes who participate in contact sports are the group most likely to suffer an MCL injury because activities such as jumping incorrectly or changing direction while running can cause the knee to twist and tear the MCL.
Symptoms an MCL tear or injury
A person with a MCL injury usually reports symptoms similar to other knee ligament injuries:
Sharp knee pain – unlike progressive knee conditions, such as knee osteoarthritis, symptoms of an MCL tear occur suddenly and can almost always be traced back to a specific incident or injury.
A popping sound – often heard at the time of the injury
Instability – this may be especially noticeable during activities that strain the knee joint, such as walking downstairs and pivoting on one leg.
Knee swelling – this usually occurs immediately after the incident/accident however, in some patients, swelling may develop up to 24 hours later and can last for up to a week.
The foot feels numb, cool or weak – This symptom needs immediate medical attention as it could also indicate a neurovascular injury.
Diagnosing an MCL tear or injury
To diagnose an MCL tear, Dr Singh will inquire about the events leading up to the injury and a physical examination of your knee will be performed. He will test your range of motion, look for swelling, and test your degree of pain which all assist with your diagnosis.
X-rays will be performed to establish if there is any bone damage, and an MRI scan may be required to evaluate the condition of your ligaments, tendons, and cartilage and to determine the extent of your injury.
It is important to remember that many conditions can cause knee pain, so a correct diagnosis in consultation with Dr Singh is critical in determining the best treatment option for you.
Treating an MCL tear or injury
MCL tears are graded by the amount of tearing in the ligament:
Grade 1 injury: The ligament is stretched, but not torn.
Grade 2 injury: Partial tear of the ligament, causes instability in the knee
Grade 3 injury: Complete tear of the ligament, causes a very unstable knee joint
For a medial collateral ligament injury that is diagnosed as a Grade 1 or 2, surgery is usually not required. Rest, bracing, physiotherapy and strengthening exercises can usually help the MCL injury to heal and if there is pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be used as directed.
Grade 3 MCL injuries that are a complete tear of the ligament will require surgery to repair and reconstruct the ligament. Tears of this type often involve other ligaments and soft tissues that may also need to be repaired.
Your treatment options can all be discussed in your consultation with Dr Singh.
 Christmas Operating Hours
Christmas Operating Hours