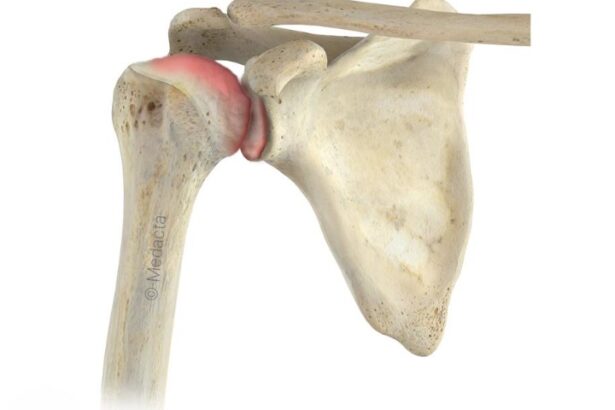
The biceps muscle is located at the front of your upper arm. The muscle has two tendons that attach it to the bones of the scapula bone of the shoulder and one tendon that attaches to the radius bone at the elbow. The tendons are tough strips of tissue that connect muscles to bones and allow us to move our limbs.
Biceps tendon injuries refer to damage to the tendons that attach the biceps muscle to the shoulder or elbow. There are two biceps’ tendons, one that attaches to the shoulder joint (long head of the biceps) and one that attaches to the elbow (short head of the biceps). Injuries to these tendons can range from mild inflammation to partial or complete tears and include:
Proximal biceps tendonitis at shoulder
Proximal biceps tendon tear at shoulder
Distal biceps tendonitis and tear at the elbow
Causes of Biceps tendon injuries
Biceps tendon injuries can be caused by a variety of factors, including overuse, repetitive motions, sudden trauma, or age-related degeneration.
Symptoms bicep tendon injuries
Symptoms of a bicep’s tendon injury may include:
Pain in the shoulder or elbow, particularly when lifting or reaching.
Weakness in the affected arm.
Tenderness or swelling around the shoulder or elbow.
A popping or snapping sensation in the arm.
Diagnosing bicep tendon injuries
Diagnosis of a biceps tendon injury typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI or ultrasound to evaluate the extent of the injury.
Treatment of bicep tendon injuries
Treatment for biceps tendon injuries may depend on the severity of the injury and the individual’s symptoms. Conservative treatments may include rest, ice, physical therapy, and medications to relieve pain and inflammation. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair a partial or complete tear of the bicep’s tendon.
The different surgical options include tenodesis, which involves reattaching the tendon to the bone using screws or other hardware, or tenotomy, which involves cutting the damaged tendon and allowing the biceps muscle to function without it. The choice of surgery will depend on factors such as the extent of the injury, your age and activity level, and other health considerations.
All of these options can all be discussed in consultation with Dr Singh.
 Christmas Operating Hours
Christmas Operating Hours