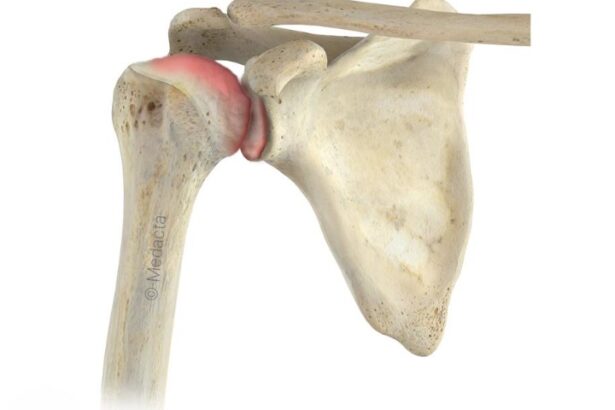
The shoulder joint is an intricate structure comprising three bones with high mobility and various muscles responsible for controlling their movements. The smaller muscles facilitate the larger ones to produce forceful shoulder and arm movements. The rotator cuff, a group of muscles, coordinates the motion between the shoulder blade and the arm. Some parts of the rotator cuff however, traverse a restricted space and can become inflamed, strained, or irritated due to swelling or narrowing of the area, leading to a condition called “impingement.” This results in the pinching of the tendon in the “subacromial space,” which causes discomfort during specific positions and movements.
The difference between shoulder impingement & shoulder bursitis
Shoulder impingement occurs when the tendons or bursa in the shoulder become compressed or pinched between the bones of the shoulder joint. This can happen due to inflammation, swelling, or other factors that reduce the space between the bones. Shoulder impingement can cause pain, weakness, and limited range of motion in the shoulder. Shoulder bursitis, on the other hand, is a condition that occurs when the bursa in the shoulder becomes inflamed. The bursa is a small sac filled with fluid that helps reduce friction between the tendons and bones in the joint. When the bursa becomes inflamed, it can cause pain, tenderness, and swelling in the shoulder.
Technically, impingement & s bursitis are therefore slightly different things, but the terms are both used to describe catching or irritation occurring inside the subacromial space.
Symptoms of a shoulder bursitis/impingement
Shoulder Bursitis and impingement is a condition usually characterised by pain, and sometimes by redness and swelling and occurs with repetitive overhead activity or overuse of the arm.
Causes of shoulder bursitis/impingement
Shoulder bursitis is typically caused by repetitive motions or activities that put stress on the shoulder joint. The condition is commonly seen in people who engage in activities that require repetitive overhead arm movements, such as throwing a ball, painting, or lifting weights. Other causes of shoulder bursitis may include:
Trauma: A direct blow to the shoulder can cause the bursa to become inflamed.
Infection: In rare cases, an infection in the bursa can lead to bursitis.
Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or thyroid disorders, can increase the risk of developing shoulder bursitis.
Age: As people age, the tendons in the shoulder can become less flexible and more prone to injury, increasing the risk of developing shoulder bursitis.
Poor posture: Poor posture can place excess stress on the shoulder joint, leading to inflammation of the bursa.
Diagnosing shoulder bursitis/impingement
Diagnosing shoulder bursitis/impingement typically involves a combination of a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests in consultation with Dr Singh:
Physical examination: During a physical examination, Dr Singh will assess the range of motion in your shoulder joint, and look for signs of swelling, tenderness, or redness in the area.
Medical history: Dr Singh will ask you about your symptoms, including when they started, how severe they are, and what activities make them worse.
Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRI scans, may be ordered to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis of shoulder bursitis/impingement.
Aspiration: If Dr Singh suspects an infection in the bursa, a sample of the fluid may be removed using a needle and sent to a lab for testing.
Treatment for shoulder bursitis/impingement
Once a diagnosis of shoulder bursitis/impingement is confirmed, treatment may involve a combination of rest, ice, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be recommended. These options will all be discussed in your consultation with Dr Singh.
 Christmas Operating Hours
Christmas Operating Hours